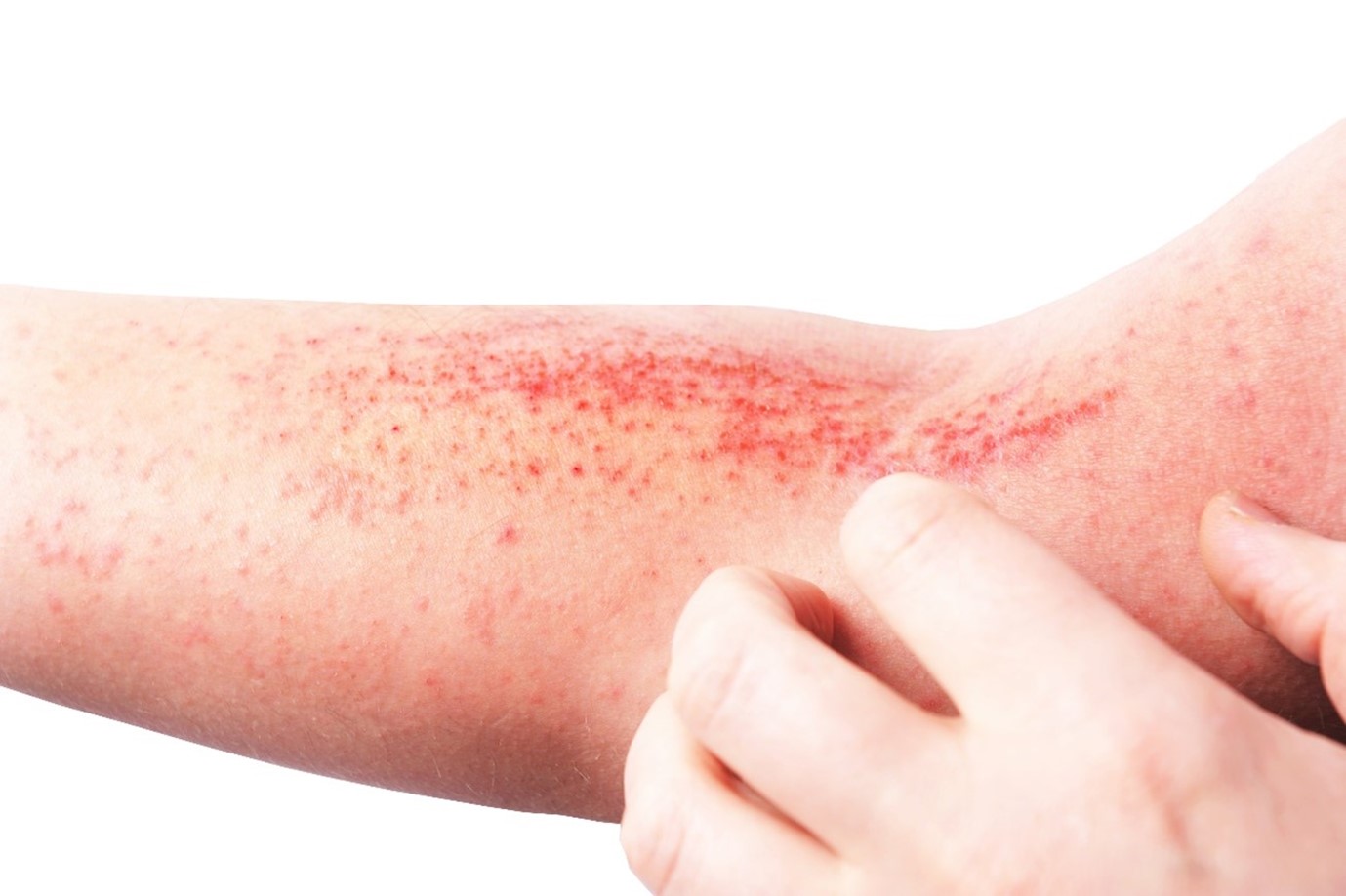
Eczema, or dermatitis, is a widespread skin condition marked by inflammation, leading to Red, Itchy, Painful areas on the skin.
Causes of Eczema
Several factors can trigger or exacerbate eczema:
- Allergens: Exposure to metals (like nickel), latex, cosmetics, or certain plants can cause allergic reactions that lead to eczema.
- Irritants: Harsh chemicals, detergents, soaps, and solvents can cause irritation and flare-ups.
- Genetics: A family history of eczema, allergic conditions, or sensitive skin increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Environmental Factors: Cold or dry weather, high humidity, and excessive sweating can all contribute to eczema.
- Stress: Emotional stress is a well-known factor that can worsen eczema symptoms.
Symptoms of Eczema
Eczema symptoms can vary but generally include:
Itching is one of the most intense and common symptoms that can worsen with scratching.
- Redness and Inflammation: Affected areas often appear red and swollen, and blisters or crusts may develop.
- Dryness and Scaling: The skin becomes dry and flaky and may crack or peel, leading to further discomfort.
- Pain and Discomfort: Eczema can cause significant discomfort, especially if the skin becomes infected.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing eczema typically involves:
- Physical Examination: The doctor will assess the skin’s appearance and the distribution of any lesions.
- Skin Patch Testing: This test is used to identify specific allergens that might trigger contact dermatitis.
- Skin Biopsy: Occasionally performed to confirm the diagnosis, especially in complex or unclear cases.
Treatment Options
Managing eczema often requires a combination of treatments to reduce symptoms and prevent flare-ups:
- Emollients: Moisturizers that hydrate the skin and protect the skin barrier.
- Corticosteroids: Anti-inflammatory creams or ointments that reduce itching and redness. Oral Medications may include antihistamines to relieve itching or antibiotics if the eczema is infected.
- Phototherapy: Limited exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light can minimize inflammation and itching in more severe cases.
Management and Prevention
Long-term management of eczema focuses on minimizing exposure to triggers and maintaining a healthy skincare routine:
- Avoid Triggers: Identifying and avoiding allergens or irritants that provoke eczema is essential for managing the condition.
- Skin Care Routine: Regularly using gentle cleansers and consistent moisturizing helps protect the skin barrier.
- Stress Management: Meditation or yoga can be beneficial in reducing stress, which may otherwise exacerbate eczema.
- Dermatologist Consultation: Regular visits to a dermatologist can help adjust treatment plans as needed and ensure the best possible care.
Don’t let eczema disrupt your life—schedule a consultation to find relief and restore your skin’s health.